To generate a good powder cure in the protection of container welds, it is important to follow a series of steps and control certain parameters:
- Rapid temperature rise: In order to properly melt the powder and keep the tin molten for as long as possible, a rapid temperature rise is sought in the furnace.
- Dwell time: Ideally, the dwell time of the container at a temperature above 232 °C (tin melting temperature) should be a minimum of 8 seconds. This ensures proper powder fusion and adhesion.
- Controlling the cooling rate: The rate at which the powder is cooled can influence the mechanical properties of the powder film. Rapid cooling will make the powder softer and more elastic, while slow cooling may cause the powder to crystallize and become more brittle.
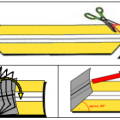
- Polymerization: It must be verified that the powder components have completed their chemical process with the help of heat, reaching a stable situation. This can be done by trimming the seam area of a container after it comes out of the oven and performing mechanical tests to ensure adhesion and integrity of the cured powder.
- Control tests: Perform varnish loading and polymerization tests to verify proper powder application and curing. These tests may include dust footprint measurements and mechanical strength tests after curing.
It is essential to follow the specific instructions of the powder manufacturer and the curing equipment to optimize the curing process and to obtain the best protective and mechanical properties of the applied powder.