A ccording to what has been defined above, we must consider the performance factors, in order to correctly evaluate the applied cost of a compound, since in addition to its wet price, which is certainly important, we must also take into account its performance for lining.
Thus, starting from the wet price, WPR, which is how the compound is purchased, we must calculate the final dry price of the compound, which is what we apply on the lid.
First, we must study the final price of the wet compound, FWPR, which will be the tariff price, minus the discounts for consumption DC, and other accumulated discounts, DF. Thus, the final wet price per kilo from which we must start will be:
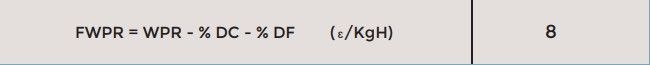
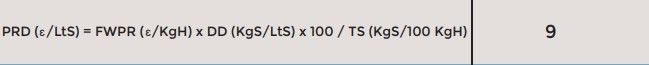
Thus, the price per dry liter, PRD, is a function of the density of the dry compound, and its percentage of soends TS:
Cost studies can also be performed for end lining as a part of the yield. One way to look at these yields is to calculate the cost of gumming one million caps. One way to look at these yields is to calculate the cost of lining one million ends. To do this, we start from the cost of lining a end, CE, which is the weight of wet compound to compound the end (in kg) times the price per kg wet end:

For one million ends, CEXM or CE (106E), we will have to multiply the above value by that amount, which results:

JOSE FCO. PÉREZ GÓMEZ
Mundolatas Advisor












0 Comments