Tuna canning is a process that preserves and prolongs the shelf life of fish, maintaining its nutritional and organoleptic properties. The tuna canning and sterilization process is essential to guarantee the quality and safety of the final product. In this article, the tuna canning process and its sterilization methods will be described in detail.
- Tuna catching and preservation
The tuna is caught at sea and kept frozen on board the ship at temperatures between -20 and -25°C (-20 and -25°F). This freezing allows the quality of the fish to be maintained until it is processed on land.
- Thawing and washing
Once on land, the tuna is thawed and washed to remove impurities and salt residues. This process is crucial to guarantee the quality and safety of the final product.
- Evisceration and classification
The tuna is eviscerated by automatic machines, and larger specimens are eviscerated manually. After evisceration, the condition of the fish is inspected. Subsequently, the tuna are sorted by size using automatic machines.
- Cooking
The fish is taken to cooking chambers where it is heated by steam at 102/103°C until a temperature of over 71°C is reached in the backbone of the pieces. The heating time depends on the size of the tuna, the capacity of the chamber and the inlet temperature of the fish.
- Cooling and cutting
Once cooked, the tuna is cooled and the heads, tails and fins are cut off and the skin is removed. The fish is then separated into two halves and then into four loins.
- Separation of dark meat
To provide a uniform quality product, the dark or bloody flesh is separated from the rest of the tuna.
- Canning
The tuna is placed in metal cans, and oil, water or sauce is added, depending on the type of canned product. The cans are then sealed to protect the contents from oxygen and microorganisms.
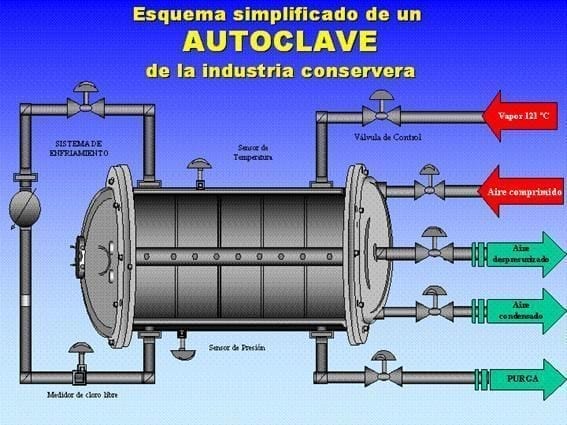
- Sterilization
The sealed cans undergo a heat sterilization process, which inactivates intrinsic and microbial enzymes. This process is essential to obtain commercially sterile products suitable for human consumption. Sterilization is performed in autoclaves at specific temperatures and times, depending on the can size and contents.
- Cooling and storage
After sterilization, the cans are cooled and stored in suitable conditions until distribution and sale.
Conclusion
The tuna canning and sterilization process is essential to guarantee the quality and safety of the final product. Proper selection of raw material, control of the process steps and adequate sterilization are key aspects to obtain high quality canned tuna suitable for human consumption.