The food canning process involves several critical steps to ensure the quality and safety of the final product. Here is a summary of the key steps based on the information provided:
- Food Preparation: Depending on the chemical and bromatological composition of the food, processes such as cold chain maintenance, sorting, washing, mixing, blanching, and precooking are carried out. These steps help prevent microbiological growth and food spoilage.
- Blanching or cooking: Vegetable products are usually subjected to blanching with hot water between 80 and 100 °C, and meat products to cooking with direct steam. This serves to shrink the food and expel gases, which is beneficial before filling the package.
- Can Cooling: After thermal processing, it is important to cool the cans properly and handle them in a manner that protects the integrity of the sealed container.
- Packaging: The containers are disinfected before use. Packaging can be manual in metal containers and is periodically verified with digital control scales.
- Pre-cooking: For some products, such as raw packaged products, a continuous stove with direct steam at temperatures of 80 to 95 °C is used.
- Addition of Topping Liquid: After packaging, the topping liquid is added to the product before sealing the containers.
- Sealing of containers: After adding the governing liquid, the containers are hermetically sealed.
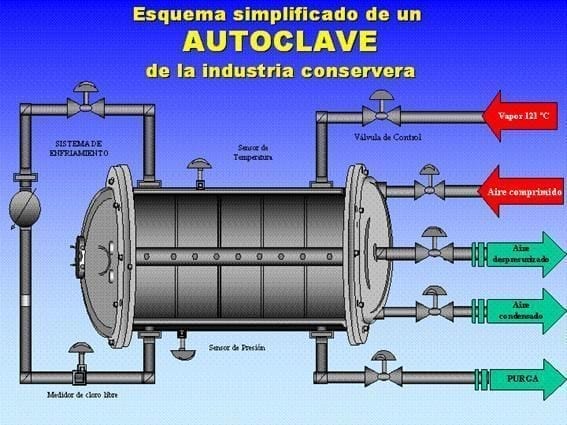
- Thermal Process: The sealed cans are subjected to a thermal process in retorts, which are pressure cookers, to achieve commercial sterility.
- Post-Thermal Process Cooling: Cans are cooled after thermal processing.
- Inspection and Packing: A final inspection is performed and then the cans are cleaned, labeled and packed for distribution.
It is important to note that each of these steps must be carried out following strict hygiene and quality control standards to avoid microbiological recontamination and ensure the safety of the canned product.













0 Comments