How to improve powder curing and adhesion to the container
Lack of powder adhesion to the container can be due to several factors. Some of the possible problems and their corrections are:
- Burner temperature too low: This can prevent proper melting of the tin, which is necessary for good powder adhesion.
- Insufficient drying time: If the drying oven does not provide the necessary time for the powder to fuse properly, adhesion will be poor.
- Unduly charged dust particle: If there is a short circuit in the dust transport, this can affect the electrostatic charge necessary for good adhesion.
- Incorrect powder feed pressure: If the pressure is too low or too high, it can affect the powder application.
- Improper fluidization in the coating tank: Improper fluidization can lead to poor powder application.
- Incorrect grounding of the can body: If the can is not properly grounded, dust particles will not adhere properly.
- Improperly adjusted absorption control valve: If the absorption control valve on the powder arm is too open or too closed, it can affect adhesion.
- Excessive distance between the can body and the conveyor belt: This can affect powder application and adhesion.
- Arm not properly oriented: Incorrect orientation of the applicator arm can lead to misapplication of powder.
- Oxidized weld: The adherence of the powder on an oxidized weld is bad, which can be the origin of powder detachment.
To solve these problems, the powder application process parameters must be adjusted and ensure that all equipment is functioning properly and that best application practices are followed.
Because the powder does not adhere well to the container
To ensure proper curing of the powder used in metal container welding protection, certain steps must be followed and several important parameters must be controlled:
- Powder Melting: A rapid rise in temperature must be achieved to properly melt the powder and keep the tin molten for as long as possible.
- Dwell Time: Ideally, the dwell time above 232 °C (melting point of tin) should be a minimum of 8 seconds or more. The fusion zone should be visible on both sides of the weld on the outside.
- Cooling Rate: The cooling rate can influence the mechanical properties of the powder film. Rapid cooling will make the powder softer and more elastic, while slow cooling can cause the powder to re-crystallize and become more brittle.
- Temperature Control: The maximum temperature reached and the time at this temperature may vary depending on the materials and thicknesses used, but in general it is between 220-250°C for 3 to 6 seconds.
- Control Tests: Control tests such as varnish loading, where the width of the powder footprint is measured and weighed to determine the amount of powder per unit area, should be performed. It is also important to check the polymerization and porosity to confirm that the varnish layer is impermeable and has completed its chemical process with the help of heat.
- Powder Preparation: Before use, it is advisable to refrigerate the powder. In addition, a fluidization process should be carried out to ensure the correct state of the powder for its application.
- Inert Atmosphere: To avoid oxidation of the weld, it is advisable to weld in an inert atmosphere by injecting nitrogen into the zone, which guarantees total elimination of oxidation in the weld.
- Equipment and Technology: Adequate equipment must be available and maintained in good condition, such as the ovens used to cure the sewing varnish and polymerize the powder. In addition, it is important to delimit the powder application area to avoid contamination to the rest of the container and the surrounding area.
By following these steps and controlling these parameters, proper powder curing can be achieved, which is essential for the protection of the weld against chemical attack and other environmental factors.
What to do for powder curing
To improve the curing process, especially in the manufacture of metal containers, some recommendations can be followed based on the information provided:
- Temperature Control: Temperature is an important factor in curing, so precise temperature control must be ensured during the curing process to guarantee proper polymerization.
- Salt concentration and acidity: In the case of food salt curing, salt concentration and acidity are crucial factors that must be carefully controlled.
- Brine Monitoring and Adjustment: The salt concentration in the brine should be monitored and adjusted when necessary to ensure fermentation control.
- Use of Appropriate Instruments: The use of indicating thermometers and other control instruments is recommended to monitor the curing process and ensure that optimum conditions are maintained.
- Preventive Maintenance: Preventive maintenance and repair of equipment is essential to avoid problems that may affect the quality of the cure.
- Innovation and Technical Support: It is beneficial to have technical support and innovation from equipment suppliers, such as autoclaves, to maintain the proper functioning of the equipment and optimize the curing process.
- Bending Speed Control: Adjusting the bending speed may be necessary to avoid problems such as trapped bodies in the bending rolls or poor overlap, which can affect the weld and thus the cure.
- Technology Watch: Keeping up to date with technological innovations can contribute to improve the curing process, using the most advanced and efficient methods and equipment.
- Equipment Calibration and Adjustment: It is important to properly calibrate and adjust equipment, such as the gauging crown on welders, to properly form the container body prior to curing.
These are some of the recommended practices to improve the curing process. It is important to keep in mind that curing is a process that may vary according to the type of product and the preservation method used, so the specific measures may vary according to the particular needs of each process.
How to improve curing
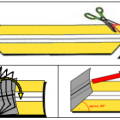
The powder film is removed by performing a bend test. This process consists of cutting two wedge-shaped pieces that reach up to the weld on both sides of the plate. The top is then bent toward the weld and brought back into place. The top is moved up and down until the plate breaks, leaving the two pieces of plate joined only by the powder weld. Finally, the lower part is clamped to the table with one hand and the upper part is pulled with the other hand at a 60° angle in the direction of the weld until the powder weld tears. The evaluation is made by measuring how far the strip of powder solder has been detached at the bottom. The maximum value of the detachment should not exceed 12 mm and after the sterilization process, 20 mm is acceptable.
Dust film is removed when pulling
To improve powder curing and container adhesion, it is important to consider several factors that can influence the process. According to the information provided:
- Powder Cooling: Before use, it is very convenient to cool the powder for a proper application.
- Isolated Application Area: To avoid dust contamination to the rest of the container and the surrounding area, it is necessary to delimit the application area by creating an enclosure as airtight as possible on the surface of the can to be protected.
- Inert Atmosphere Welding: Perform welding by injecting nitrogen into the zone to ensure total elimination of oxidation in the zone, provided that dust protection is carried out afterwards.
- Parameter Control: Basic parameters such as varnish load, polymerization, porosity and autoclave behavior should be controlled to verify a good application of powder varnish.
- Powder Composition: Powder composition is important, and proper selection of resins, curing agents, additives, post-additives, dye pigments and extenders should be considered to obtain the desired application characteristics.
- Avoid Rusting: Adhesion of already cured powder on an oxidized weld is poor, so oxidation should be avoided prior to powder application.
- Inspection and Quality Control: It is important to perform inspections and quality controls, such as electrotesting and weld porosity analysis, to ensure the correct application and curing of the powder.
- Use of Appropriate Technology: Electrostatic powder coating technology has proven to be effective, as it involves the electrostatic deposition of very small solid particles onto the substrate, followed by a cure that melts the particles into a continuous film.
Implementing these practices can significantly improve powder curing and adhesion to the container, which is crucial for the protection of the container weld against chemical attack and other environmental factors.